Introduction
NVMe SSDs have become the standard for high-speed storage in both personal and professional environments. However, not all NVMe SSDs are created equal. Consumer and enterprise-grade NVMe drives differ significantly in durability, performance, and features.
This blog explains the core differences to help you choose the right drive for your use case.
What Is an NVMe SSD?
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a storage protocol designed specifically for solid-state drives connected via PCIe. Compared to SATA-based SSDs, NVMe provides faster read/write speeds, lower latency, and higher parallelism through multiple queues.
NVMe SSDs achieve these improvements through direct connection to the PCIe bus, bypassing traditional SATA controllers. Key advantages include:
- Up to 6-7x faster sequential read/write speeds compared to SATA SSDs
- Reduced protocol overhead and improved efficiency
- Better power efficiency per operation despite higher performance
This makes NVMe drives ideal for applications requiring fast data access, and why many devices now opt for the NVMe protocol for storage, such as OS boot drives, gaming, content creation, and enterprise databases.
Use Case Differences
The distinction between consumer and enterprise NVMe SSDs ultimately comes down to their intended applications and operating requirements. While both types leverage the same basic NVMe protocol, they are optimized for very different use cases.
Consumer NVMe SSDs are designed for personal computing environments where cost-effectiveness and peak performance matter most. These drives excel in:
- Gaming and entertainment applications
- General office productivity tasks
- Content creation and media editing
- Home server and personal backup storage
Enterprise NVMe SSDs, on the other hand, are engineered for demanding professional environments that require unwavering reliability. Their primary applications include:
- High-traffic database servers
- Cloud computing infrastructure
- Virtual machine hosts
- Mission-critical storage systems
Key Technical Differences
Feature | Consumer SSDs | Enterprise SSDs |
Endurance | Lower TBW Ratings - Sufficient for day-to-day tasks | Higher TBW ratings - Supports constant write activity |
Performance | May throttle under sustained loads | Stable IOPS and latency under high loads |
Power Protection | Usually no capacitors | Built-in power loss protection |
Overprovisioning | Minimal spare capacity | Extra capacity for wear leveling |
Enterprise Features | Typically used only for BootOS | End-to-end data protection
|
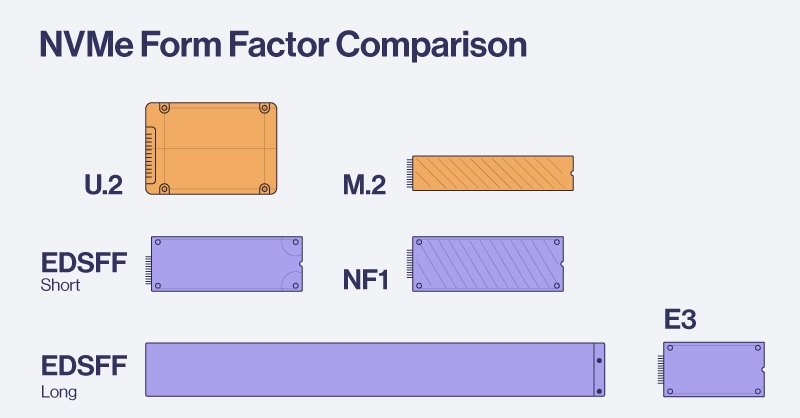
Form Factor | Primarily M.2 format | U.2, U.3, E1.S, E3 for servers |
Cost and Value
When comparing storage solutions, both consumer and enterprise NVMe SSDs offer distinct advantages tailored to different use cases. Consumer NVMe SSDs provide excellent value for everyday computing needs, while enterprise drives come at a price premium, engineered for constant intensive workloads.
Consumer NVMe SSDs excel in:
- Cost-effective performance for daily computing tasks
- Ideal for gaming and content creation workflows
- Excellent speed-to-price ratio
- Performance can degrade under heavy load
- Perfect for home and small business use
Enterprise NVMe SSDs offer:
- Enhanced durability for 24/7 operation
- Advanced data protection features
- Consistent performance under heavy workloads
- Specialized features for datacenter environments
Conclusion
Consumer and enterprise NVMe SSDs may look similar, but they’re engineered for very different purposes. For light to moderate usage, consumer drives offer speed and value. For demanding workloads where reliability and uptime matter, enterprise SSDs deliver the features and durability needed to support mission-critical systems.
At SabrePC, we build custom server solutions ranging from GPU-compute servers to NVMe storage. Contact us today for more information or visit our solution pages and configure a system today.