What is computer memory?
A computer memory stores information, which has to be accessed immediately either from temporary memory slots or from permanent storage locations. In general, computer memory can be classified into two types:
- Primary memory
- Secondary memory
Primary Memory
Whenever you turn on the computer, it makes use of the primary memory to load the operating system, user interface, and all other software utilities. In this sense, primary memory is accessed directly by the processor to load running applications that exist in specific temporary memory slots. Furthermore, all tasks that are application-specific, are performed due to the interaction of the primary memory with the system’s processor.
RAM (Random Access Memory)
Abbreviated as RAM, Random Access Memory is a good example of primary memory. The Central Processing Unit (CPU) makes use of the RAM to store all information that needs to be accessed immediately. However, this information is stored temporarily in specific memory slots since RAM is a volatile memory. This implies that if a power failure occurs while a task is being performed, all your unsaved data will be lost! Unfortunately, recovery would nearly be impossible.
RAM can further be classified into the following types.
- DRAM
- SRAM
- DRDRAM
ROM (READ ONLY MEMORY)
Abbreviated as ROM, Read-Only Memory is another example of primary memory, which is non-volatile in nature. It retains all information in permanent memory slots, even if the power goes off. These integrated circuits are programmed with the particular information at the time of its manufacture.
The following are some types of ROM:
- PROM: Programmable Read-Only Memory (PROM) is a type of ROM that is programmable, only once. This type of ROM uses a microcode, tailored by a user through a PROM programmer. This program is stored permanently and cannot be erased.
- EPROM: The EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) offers some solutions to the problems that are associated with a PROM. In comparison to the PROM, the EPROM allows data deletion by passing ultraviolet light. Once erased, the EPROM can be programmed again.
- EEPROM: EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) has the same functionality as EPROM, with the only difference that it requires an electrical beam to erase the data.
Secondary Memory
Secondary memory is a type of memory stored externally in a storage medium and is permanent in nature. This is where all the data and programs are saved for lengthy periods of time. The hard drive is a good example of a secondary memory device, which has a huge storage capacity as compared to the computer’s main memory. Magnetic disks, magnetic tapes, SSDs, and USB memory drives are all examples of secondary memory media.
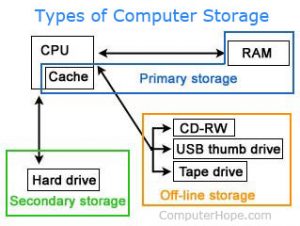
Why does the computer need a primary memory?
The primary memory allows the CPU to access information and data quickly, allowing you to surf through applications and installed programs effortlessly. If the CPU had to access this information from the secondary storage every single time, the performance of the system would slow down massively.
How important is computer memory?
Computer memory is analogous to your brain. It contains all the vital information (data), along with instructions needed to process that very information! Without a computer memory, it would nearly be impossible for a computer to carry out even the simplest of all tasks such as ‘copy/cut and paste’.